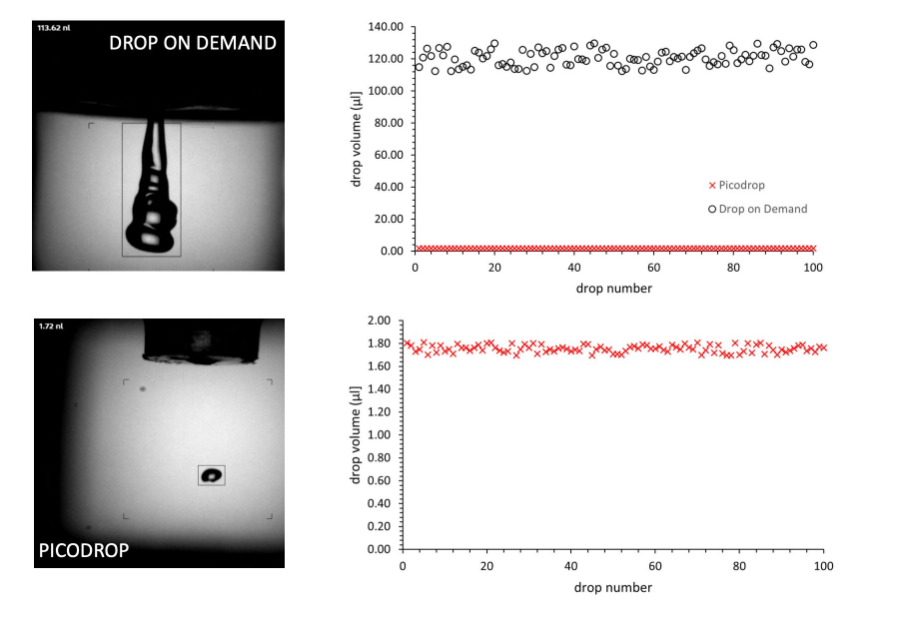
NMI, TU Darmstadt and Black Drop develop improved bioink
3D bioprinting: improved nutrient transport in printed tissue Researchers at the NMI Natural and Medical Sciences Institute in Reutlingen, TU Darmstadt and Black Drop Biodrucker[…]

New Bioink Improves Nutrient Transport in 3D-Printed Tissue
The 3D bioprinting sector faces the challenge of creating tissue that realistically replicates the complex anatomy of human organs. Researchers from the NMI Natural and Medical[…]

3D-bioprinted capillary-like networks as versatile organ-on-a-chip platform
Last month, the 44th Annual Conference of the European Society for Artificial Organs was held in Vienna. The conference offered a diverse program with impressive talks and[…]
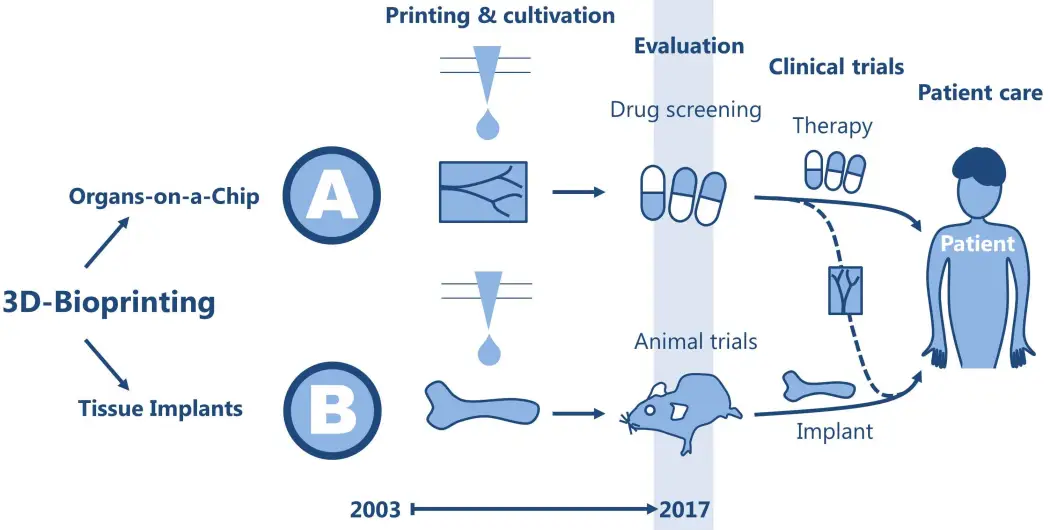
Bioprinting in Clinical Research
Bioprinting has the potential to improve clinical research and patient care in multiple ways. After a decade of technological advancements its way to the clinics has[…]